The below playbook will log into tomcat server Create a folder called Downloads. Download artifact into it and copy them into the /var/lib/tomcat8/webapps
DevOps Training Program that will provide you with in-depth knowledge of various DevOps tools including Git, Jenkins, Docker, Ansible, Puppet, Kubernetes and Nagios. This training is completely hands-on and designed in a way to help you become a certified practitioner through best practices in Continuous Development, Continuous Testing, Configuration Management and Continuous Integration, and finally, Continuous Monitoring of software throughout its development life cycle.
Saturday, 20 February 2021
Deploying with Ansible Tower( Playbook to deploy artifact to tomcat)
Datadog - Continuous Monitoring
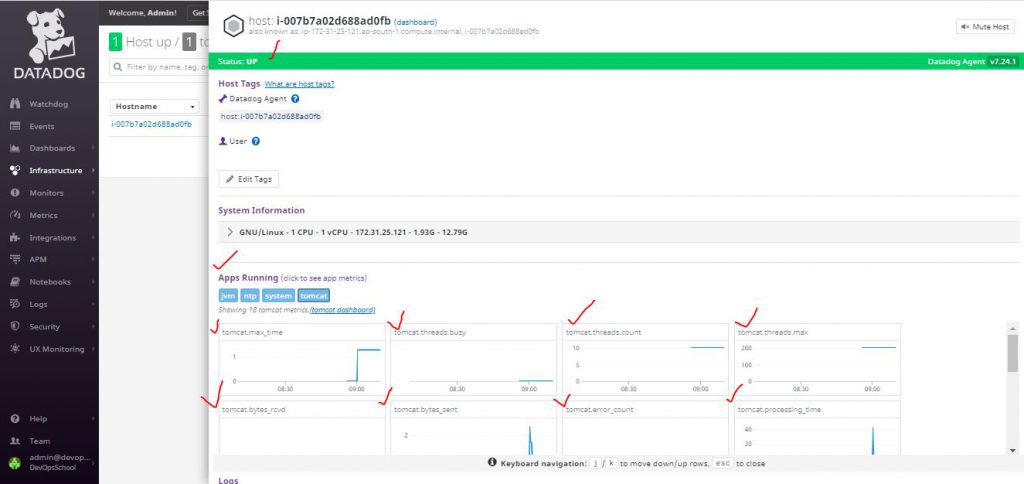
How to enable Apache Tomcat monitoring in Datadog Agent
Apache Tomcat Integratoion with Datadog collects Following Tomcat metrics
- Overall activity metrics: error count, request count, processing times, etc.
- Thread pool metrics: thread count, number of threads busy, etc.
- Servlet processing times
Step 1 – Sign up for a Datadog Account
Step 2: Install the datadog Agent on your Tomcat Server
Select your OS:Ubuntu
Then copy the command in the box:Use our easy one step install
Log into your Tomcat server and paste and run the command to install datadog agent
DD_AGENT_MAJOR_VERSION=7 DD_API_KEY=4cf1ee64a11f9c21c2020b85376e552c DD_SITE="datadoghq.com" bash -c "$(curl -L https://s3.amazonaws.com/dd-agent/scripts/install_script.sh)"
Select your host: And you should see the metric graphs
Saturday, 23 January 2021
Nagios – Continuous Monitoring
What is Nagios?
Nagios is used for Continuous monitoring of systems, applications, services, and business processes etc in a DevOps culture. In the event of a failure, Nagios can alert technical staff of the problem, allowing them to begin remediation processes before outages affect business processes, end-users, or customers. With Nagios, you don’t have to explain why an unseen infrastructure outage affect your organization’s bottom line.
Nagios runs on a server, usually as a daemon or a service.
It periodically runs plugins residing on the same server, they contact hosts or servers on your network or on the internet. One can view the status information using the web interface. You can also receive email or SMS notifications if something happens.
The Nagios daemon behaves like a scheduler that runs certain scripts at certain moments. It stores the results of those scripts and will run other scripts if these results change.
Plugins: These are compiled executables or scripts (Perl scripts, shell scripts, etc.) that can be run from a command line to check the status or a host or service. Nagios uses the results from the plugins to determine the current status of the hosts and services on your network.
Let’s now discuss it’s architecture.
Nagios Architecture:
- Nagios is built on a server/agents architecture.
- Usually, on a network, a Nagios server is running on a host, and Plugins interact with local and all the remote hosts that need to be monitored.
- These plugins will send information to the Scheduler, which displays that in a GUI
Following are the important features of Nagios monitoring tool:
- Relatively scalable, Manageable, and Secure
- Good log and database system
- Informative and attractive web interfaces
- Automatically send alerts if condition changes
- If the services are running fine, then there is no need to do check that host is an alive
- Helps you to detect network errors or server crashes
- You can troubleshoot the performance issues of the server.
- The issues, if any, can be fixed automatically as they are identified during the monitoring process
- You can monitor the entire business process and IT infrastructure with a single pass
- The product's architecture is easy writing new plugins in the language of your choice
- Nagios allows you to read its configuration from an entire directory which helps you to decide how to define individual files
- Utilizes topology to determine dependencies
- Monitor network services like HTTP, SMTP, HTTP, SNMP, FTP, SSH, POP, etc.
- Helps you to define network host hierarchy using parent hosts
- Ability to define event handlers which runs during service or host events for proactive problem resolution
- Support for implementing redundant monitoring hosts
wget https://sourceforge.net/projects/nagios/files/nagios-4.x/nagios-4.3.2/nagios-4.3.2.tar.gz
wget https://nagios-plugins.org/download/nagios-plugins-2.2.1.tar.gz
tar -zxvf nagios-4.3.2.tar.gz
tar -zxpvf nagios-plugins-2.2.1.tar.gz
useradd nagios
passwd nagios
groupadd nagcmd
usermod -G nagcmd nagios
usermod -G nagcmd apache
cd nagios-4.3.2
./configure --with-command-group=nagcmd
make all
make install
make install-init
make install-commandmode
make install-config
make install-webconf
htpasswd -s -c /usr/local/nagios/etc/htpasswd.users nagiosadmin
systemctl restart httpd
cd ..
cd nagios-plugins-2.2.1/
./configure --with-nagios-user=nagios --with-nagios-group=nagios
make
make install
/usr/local/nagios/bin/nagios -v /usr/local/nagios/etc/nagios.cfg
systemctl enable nagios
systemctl start nagios
systemctl restart httpd
systemctl restart nagios
open the browser http://ip address/nagios
uid:nagiosadmin(set in the previous steps)
pwd: nagios
cd /usr/local/nagios/ ls cd etc/
vi nagios.cfg
# then uncomment this line /usr/local/nagios/etc/servers
On Nagios Host (linux):
rpm -ivh https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-7.noarch.rpm
yum install nrpe nagios-plugins-all -y
vim /etc/nagios/nrpe.cfg
# enter edit model by pressing i and replace the server ip with with the node private ip and Host ip with Nagios Master with the private ip
systemctl start nrpe
let do some exercise by installing LAMP on the Host
sudo yum update -y
sudo amazon-linux-extras install -y lamp-mariadb10.2-php7.2 php7.2
cat /etc/system-release
sudo yum install -y httpd mariadb-server
yum info package_name
sudo systemctl start httpd
sudo systemctl enable httpd
sudo systemctl is-enabled httpd
#log into the master server with the following
cd /
cd var
cd log
cat yum.log
Thursday, 14 January 2021
Ansible Open Source
What Is Ansible?
A task could be Installing NGINX webserver, for example.
In Ansible, we name a task and write down the command we want it to execute.
A task can be part of bigger thing like bringing up our e-commerce website.
Other tasks like applying updates, adding our custom config file can also be added.
The bigger thing or a group of tasks is grouped in what we call a Playbook.
A Playbook is just a file where we tell Ansible the tasks we want it to execute in an orderly fashion.
Ansible doesn't depend on additional daemons, client or servers.
The mechanics of Ansible
A Control node (that has Ansible installed) reads a Playbook file and executes the tasks listed in the playbook.
We also mention in the playbook the host or group of hosts where such tasks should be executed.
The inventory file is where we have a list of individual hosts.
We can group individual hosts into groups within the Inventory file.
In the example below, we execute ansible-playbook <playbook_name> command on Ansible control node (10.10.10.100).
It then reads a Playbook file that has 2 tasks.
Task1 is executed on DBServers group of hosts and Task2 on WebServers group:
Ansible Terms:
- Controller Machine: The machine where Ansible is installed, responsible for running the provisioning on the servers you are managing.
- Inventory: An initialization file that contains information about the servers you are managing.
- Playbook: The entry point for Ansible provisioning, where the automation is defined through tasks using YAML format.
- Task: A block that defines a single procedure to be executed, e.g. Install a package.
- Module: Ansible modules are discrete units of code which can be used from the command line or in a playbook task.
- Role: A pre-defined way for organizing playbooks and other files in order to facilitate sharing and reusing portions of a provisioning.
- Play: A provisioning executed from start to finish is called a play. In simple words, execution of a playbook is called a play.
- Facts: Global variables containing information about the system, like network interfaces or operating system.
- Handlers: Used to trigger service status changes, like restarting or stopping a service.
ANSIBLE ARCHITECTURE
Ansible installation on linux AWS
Step1:
Launch Two (Amazon Linux 2) Aws instances(one will be the controller, the other will be the Target host)
Step 2:
On The Target host machines Set password Authentication:
Switch to root user
sudo su -
Then edit the sshd_config file to enable password authentication
vi /etc/ssh/sshd_config
look for the below line and change the entry from no to yes
PasswordAuthentication yes
#PermitEmptyPasswords no
#PasswordAuthentication no
Next Create a password for ec2-user
passwd ec2-user
#then enter the password twice and press enter(you can use admin123)
Note: The password will not show on the screen as u type it. Just type and press enter when u are done
Next Edit the sudoers file to enable ec2-user have full previledges
vi /etc/sudoers
Insert the below line in the editor and save
ec2-user ALL=NOPASSWD: ALL
Save ---> :wq!
Next restart the ssh service with below command
systemctl restart sshd
Step 3:On Ansible Controller machine Install Ansible
Switch to root
sudo su -
Install Ansible
sudo yum update -y
sudo yum install ansible -y
ansible --version
Next edit the hosts file which will contain inventory of all ur target hosts and add ur target host ip
vi /etc/ansible/hosts
Uncomment [webservers] delete the entries under it and Add ip of Target host under it
Save then switch to ec2-usersu - ec2-user
Generate a keypair
ssh-keygen -t ed25519#Press enter four times to generate ssh key to connect the hosts machine
Next send the public key of the Ansible Controller to the target machine by executing this command
ssh-copy-id ec2-user@ipofansiblehost
eg ssh-copy-id ec2-user@192.168.25.1
You will be prompted for password. Enter ur password: admin123
Now try and connect to the target host
ssh ec2-user@ipofansiblehost
eg ssh ec2-user@192.168.25.1
Then exitexit
#check for remote connection to your hosts machine with below commandansible -m ping webservers
1. The Anatomy of the Command
ansible: This invokes the Ansible command-line tool for "ad-hoc" commands (one-off tasks that don't require a full playbook).
-m ping: This tells Ansible to use the ping module.
Note: This is not an ICMP ping (like the one you use in a terminal to check if an IP is alive). It is a Python-based check that logs into the server via SSH and verifies that Python is installed and usable.
webservers: This is the pattern or group name. Ansible looks into your inventory file (usually located at /etc/ansible/hosts or a local hosts.ini) and runs the command against every server listed under the [webservers] header
#Ansible Module: A module is a command or set of similar Ansible commands meant to be executed on the client-side
#
ansible: This invokes the Ansible command-line tool for "ad-hoc" commands (one-off tasks that don't require a full playbook).-m ping: This tells Ansible to use the ping module.Note: This is not an ICMP ping (like the one you use in a terminal to check if an IP is alive). It is a Python-based check that logs into the server via SSH and verifies that Python is installed and usable.
webservers: This is the pattern or group name. Ansible looks into your inventory file (usually located at/etc/ansible/hostsor a localhosts.ini) and runs the command against every server listed under the[webservers]header
Understanding Ansible Modules
Modules perform tasks remotely.
Example:
Create user:
ansible webservers -m user -a "name=devops" --become
Install package:
ansible webservers -m yum -a "name=httpd state=present" --become
Start service:
ansible webservers -m service -a "name=httpd state=started" --become
Think of --become as the Ansible equivalent of typing sudo before a command in a Linux terminal.
When you add --become to your command:
Ansible connects as your normal user (e.g., ec2-user).
It then "becomes" another user (by default, root) to execute the specific task.
Once the task is finished, it drops those privileges.
Think of --become as the Ansible equivalent of typing sudo before a command in a Linux terminal.
When you add --become to your command:
Ansible connects as your normal user (e.g.,
ec2-user).It then "becomes" another user (by default, root) to execute the specific task.
Once the task is finished, it drops those privileges.
2. Example Comparison
If you want to install Apache on your webservers, a normal user doesn't have the "keys" to the system's package manager.
This will fail:
ansible webservers -m yum -a "name=httpd state=present"
(Error: You need to be root to perform this command.)
This will succeed:
ansible webservers -m yum -a "name=httpd state=present" --become
(Success: Ansible uses sudo to install the package.)
Let's use some playbooksudo vi playbook.ymlInsert the below lines into the playbook---- name: Install Web Server hosts: webservers become: true
tasks:
- name: Install HTTPD yum: name: httpd state: present
- name: Start HTTPD service: name: httpd state: started enabled: yesSave with :wq!#check for syntax errors with below commandansible-playbook playbook.yml --syntax-check
#do a dry run with below command
ansible-playbook playbook.yml --check
sudo vi playbook02.yml
Paste the below lines into the editor and save---- hosts: webservers become: true
tasks:
- name: Install Apache yum: name: httpd state: present
- name: Deploy index file copy: content: "Hello from Ansible Automation" dest: /var/www/html/index.html notify: restart apache
handlers:
- name: restart apache service: name: httpd state: restartedopen port 80
If you want to install Apache on your webservers, a normal user doesn't have the "keys" to the system's package manager.
This will fail:
ansible webservers -m yum -a "name=httpd state=present"
(Error: You need to be root to perform this command.)
This will succeed:
ansible webservers -m yum -a "name=httpd state=present" --become
(Success: Ansible uses sudo to install the package.)
🧠 Important Ansible Concepts
✅ Inventory
Defines servers.
webservers
dbservers
k8snodes
Defines servers.
webservers
dbservers
k8snodes
✅ Playbook
Automation workflow written in YAML.
Automation workflow written in YAML.
✅ Tasks
Individual automation steps.
Individual automation steps.
✅ Modules
Examples:
Module Purpose yum Install packages service Manage services copy Transfer files user Create users git Clone repos
Examples:
| Module | Purpose |
|---|---|
| yum | Install packages |
| service | Manage services |
| copy | Transfer files |
| user | Create users |
| git | Clone repos |
✅ Handlers
Triggered only when changes occur.
Triggered only when changes occur.
✅ Become
Privilege escalation (sudo).
become: true
Privilege escalation (sudo).
become: true
🏗️ REAL DEVOPS USE CASES
Students can automate:
✅ Jenkins installation
✅ Docker setup
✅ Kubernetes nodes
✅ Tomcat deployment
✅ NGINX configuration
✅ Application rollout
Students can automate:
✅ Jenkins installation
✅ Docker setup
✅ Kubernetes nodes
✅ Tomcat deployment
✅ NGINX configuration
✅ Application rollout
SECURITY BEST PRACTICES (IMPORTANT)
✅ Use SSH keys only
✅ Restrict Security Groups
✅ Avoid password authentication
✅ Avoid root login
✅ Use private subnets for automation
✅ Use SSH keys only
✅ Restrict Security Groups
✅ Avoid password authentication
✅ Avoid root login
✅ Use private subnets for automation
Bash Script To Install Ansible Automation Platform ( AWX)
#!/bin/bash # --- Configuration --- AWX_OPERATOR_VERSION="2.19.1" NAMESPACE="awx" KUBECONFIG_PATH="/etc/rancher/k3s...
-
Please follow steps to install Java, Jenkins, Maven, Tomcat on Ubuntu EC2. Jenkins is a java based application, so you need to install Jav...
-
pre-requisites: 1. Make sure you configure maven installation under Jenkins-->manage Jenkins-> Global Tool Config...
-
We will see how to setup Java Web App using Maven in BitBucket and also how to setup SSH keys in Bitbucket. Pre-requistes: If you don'...































